- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

The NASA aerospace agency approved and allocated funds for the first stage of designing a new space telescope with a mirror diameter of 30 meters. But the most interesting in this project is not even the giant size of the device, but its assembly feature. According to the plans, the parts of the telescope will be launched on different rockets and will independently gather in orbit into a single whole.
Since the time of Galileo, the main enemy of terrestrial astronomy has been small movements of atmospheric air, which did not allow us to obtain an image in subtle detail. But now they have learned to fight with this using adaptive optics. In conditions of the prohibitive cost of space launches, it became easier to build a very large telescope on the Earth than to put a smaller instrument into orbit.
The draft team of Dmitry Savransky from Cornell University refutes this opinion. According to the author of the project, there is no need to run one large device into orbit when it is possible to send many small ones into space.
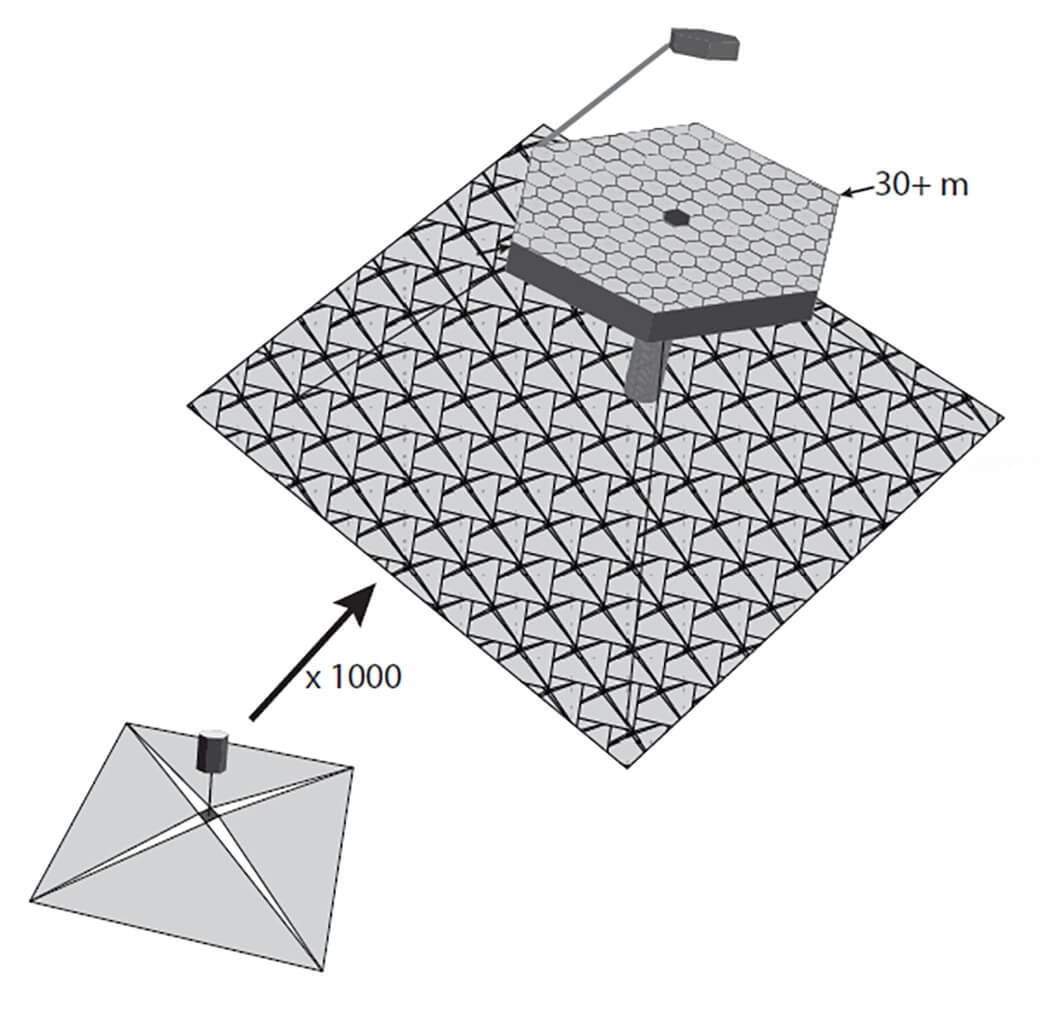
The mirror of the new telescope itself will be assembled in orbit from individual modules
For several months or even years into orbit, it will be possible to output individual elements of the future mirror - hexagons about the size of about a meter. For this, even separate rocket launches will not even be required: each new part of the vehicle can be launched into orbit together with another main cargo.
It is expected that each part of the telescope will be supplied with a space sail, which will allow it to move under the influence of the solar wind. Moreover, the solar sails of each element together form a kind of sun screen for the new telescope. Gathered at the second point of Lagrange, all these elements will be connected to a huge 30-meter telescope. The size, it should be noted, is impressive - far from many ground-based telescopes are ready to boast such a size of their main mirrors, not to mention space "babies" "Hubble", whose mirror diameter is only 2.4 meters, and the new infrared telescope "James Webb "With a mirror diameter of 6.5 meters.
According to the plans presented on the project site, the telescope can work in the infrared, optical and ultraviolet ranges.
As noted on the NASA website, the project of the 30-meter space telescope has become one of the winners of the first phase of the annual contest NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (Advanced Innovative Concepts NASA, NIAC). Developers were allocated about 125 thousand US dollars and nine months for further calculations.
The project of assembling a tool from small autonomous modules in the coming epoch of miniature spacecraft does not look so fantastic. Well, the potential of the new telescope is impressive even for scientists who do not take part in its development.
"If Professor Savransky proves the feasibility of creating a large space telescope from tiny pieces, it will change the way we explore the cosmos," says Mason Peck of Cornell University.
"We can afford to see further and better than ever, perhaps even to see the surface of exoplanets."
The article is based on materials .
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment